Millions of individuals worldwide are dealing with the long-term effects of diabetes. Its impact on blood sugar and consequences, including cardiovascular disease and neuropathy, is well-known, but its impact on eye health is less so.
This blog post discusses the link between diabetes and eye disorders, outlining the dangers, symptoms, and preventative measures to take.
Diabetes and Its Impact on Eye Health
Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic condition and a lifestyle disorder affecting millions of people worldwide. While insulin is well-known for its influence on blood sugar levels and possible problems like heart disease and neuropathy, one area of worry that is less well-known is its effect on eye health.
This blog piece discusses the connection between diabetes and eye disorders, emphasizing the potential hazards, warning indications, and necessary procedures to protect your vision.
Diabetic Eye Diseases
Diabetic Retinopathy:
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a consequence of diabetes that causes vision loss in the macula. Fluid leaks into the macula when blood sugar levels are high, causing central vision to enlarge and become distorted. Because of this disorder, a person may have trouble reading, recognizing faces, and doing other fine-tuned visual tasks.
Diabetic Macular Edema (DME):
DME is a specific condition of diabetic retinopathy that affects the macula, which is in charge of central vision. When blood sugar levels are too high, fluid leaks into the macula. This makes the macula swell and messes up the centre’s vision. This problem can make it hard to read, recognize faces, or do other things that require fine vision.
Cataracts:
People with diabetes are at increased risk of getting cataracts – a clouding of the eye’s natural lens that leads to blurred vision. Cataracts can progress faster in people with diabetes, leading to visual impairment.
Glaucoma:
Glaucoma or Kalamotia damages our optic nerve and could lead to visual loss; diabetes can raise the chance of developing these conditions. The risk of developing Glaucoma in people with diabetes is increased by a factor of 2.
Symptoms & Warning Signs of Eye Diseases
Early detection is crucial in managing diabetic eye diseases effectively. Be vigilant about the following warning signs.
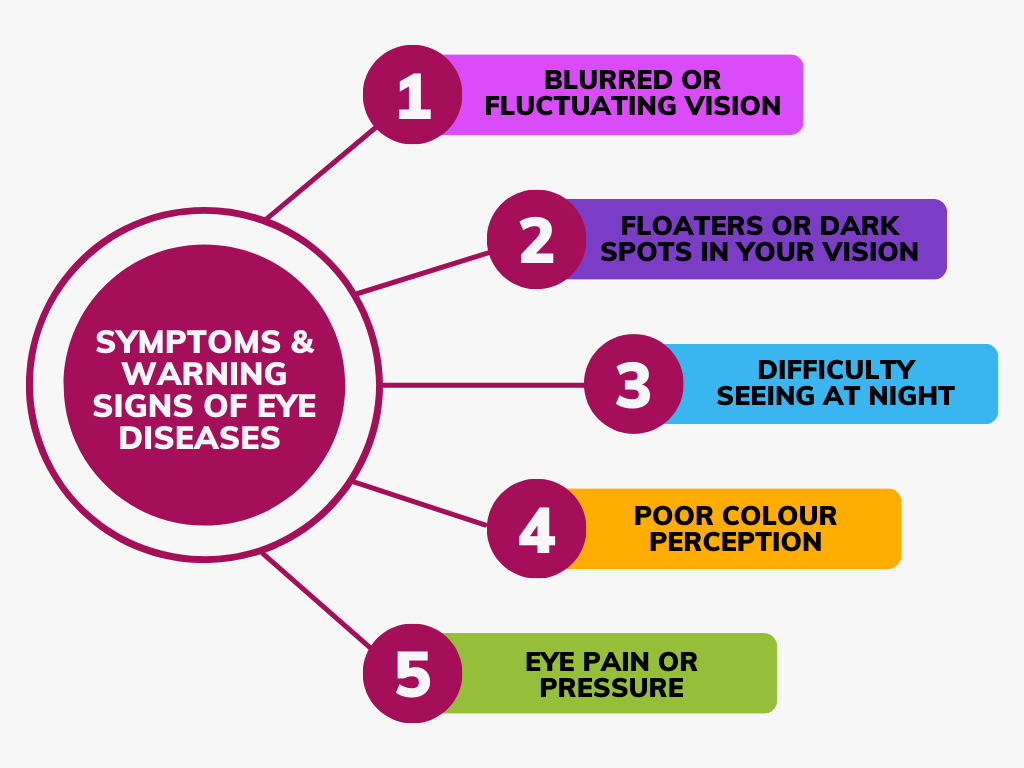
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Floaters or dark spots in your vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Poor colour perception
- Eye pain or pressure
- Gradual loss of peripheral vision
Preventive Measures and Management
Regular Eye Examinations: If you have diabetes, regular eye check-ups are paramount. The American Diabetes Association advises a comprehensive eye exam at least once a year. These exams can help identify potential eye issues early on, allowing for timely intervention.
Control Blood Sugar Levels: Diabetes can raise the risk of Glaucoma, a set of eye disorders that cause optic nerve damage and visual loss. Diabetes patients are at twice the risk as non-diabetics of getting Glaucoma.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can worsen diabetic eye diseases. Quit smoking and limit alcohol intake to protect your vision.
Follow Your Doctor’s Recommendations: If you are diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy or other eye conditions, follow your eye specialist’s advice diligently. Laser therapy, injections, or surgery may be necessary to preserve your vision.
Blog Summary
Diabetes is a lifestyle disorder and complicated disease that can affect several parts of your health, including your eyes. Diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema (DME), cataracts, and glaucoma are just a few of the diabetes-related eye illnesses that can lead to significant vision loss if they are not addressed. People with diabetes can better protect their eye health and lower their chance of losing sight if they are proactive, control their blood sugar levels, get regular eye exams, and listen to professional advice. Remember that early discovery and quick action are essential to keep your sight for life.